Exercise 4 Review Sheet the Cell Anatomy and Division
1
Define the following term:
Organelle
"small organs"; are the metabolic machinery of the jail cell, and that are highly organized to deport out specific functions for the cell as a whole.
two
Define the following term:
Cell
the structural and functional unit of all living things, is a complete entity.
three
Although cells accept differences that reflect their specific functions in the trunk, what functions do they accept in common?
Growing, reproducing, and responding to a stimulus are common functioning characteristics amidst all cells. In add-on, all cells can maintain their boundaries, metabolize, digest nutrients, and dispose wastes
external purlieus of prison cell; regulates flow of materials into and out of the cell; site of cell signaling
contains digestive enzymes of many varieties; "suicide sac' of the cell
scattered throughout the prison cell; major site of ATP synthesis
slender extensions of the plasma membrane that increment its surface area
stored glycogen granules, crystals, pigments, and so on
membranous system consisting of flattened sacs and vesicles; packages poly peptide for export
command heart of the prison cell; necessary for cell sectionalisation and cell life
two rod-shaped bodies near the nucleus; directly formation of the mitotic spindle
dense, darkly staining nuclear torso; packaging site for ribosomes
contractile elements of the cytoskeleton
fourteen
Crude ER or endroplasmic reticulum
membranous system; involved in intracellular transport of proteins and synthesis of membrane lipids
attached to membrane systems or scattered in the cytoplasm; synthesize proteins
16
Chromatin or Chromatin threads
threadlike structure in the nucleus; incorporate genetic cloth (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
site of free radical detoxification
18
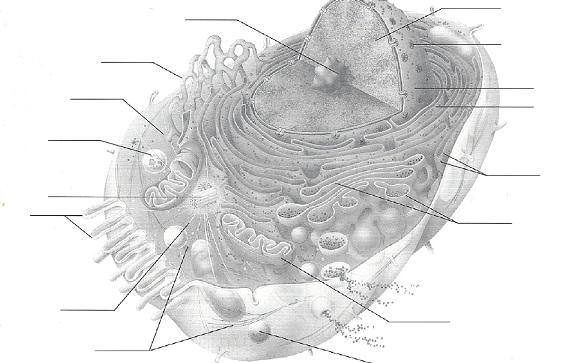
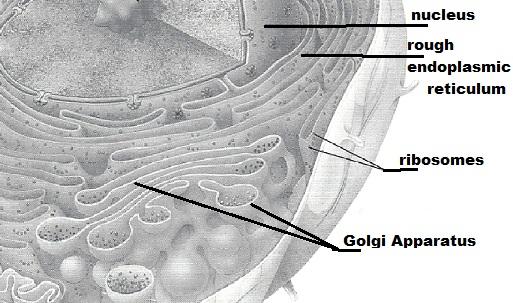
In the following diagram, label all parts provided with a leader line.
I bankrupt the moving-picture show downwards cause it was non big enough to fit, they are in the following slide...
19
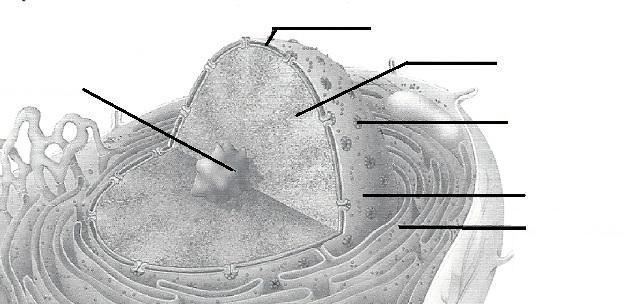
PUT YOUR MOUSE OVER Prototype TO Enlarge

PUT YOUR MOUSE OVER IMAGE TO Enlarge
20

PUT YOUR MOUSE OVER IMAGE TO ENLARGE

PUT YOUR MOUSE OVER IMAGE TO ENLARGE
21
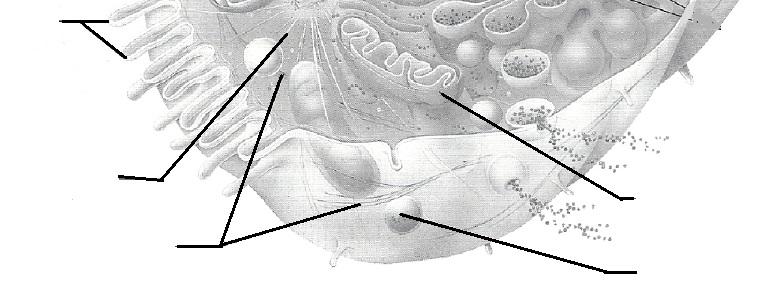
PUT YOUR MOUSE OVER Image TO ENLARGE
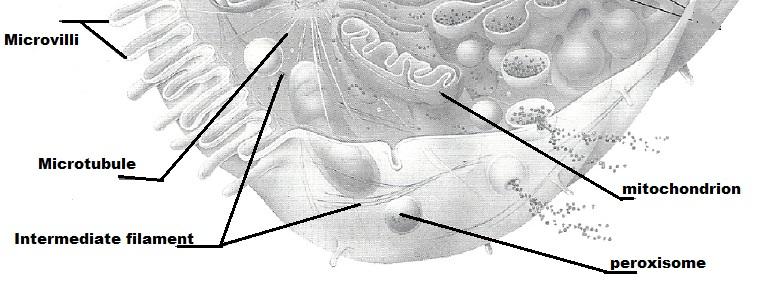
PUT YOUR MOUSE OVER Paradigm TO ENLARGE
22

PUT YOUR MOUSE OVER Epitome TO Overstate
PUT YOUR MOUSE OVER IMAGE TO Enlarge
23
For each of the post-obit cell types, listing (a) 1 important structural characteristic observed in the laboratory, and (b) the function that the construction complements or ensures.
squamous epithelium
a.__________________________________________
b.__________________________________________
squamous epithelium tissue-
a) flat shaped
b) good for layering and overlapping.
24
For each of the following jail cell types, list (a) one of import structural characteristic observed in the laboratory, and (b) the part that the construction complements or ensures.
sperm
a.______________________________________________
b.______________________________________________
sperm-
a) flagella
b) allows the cell to be mobile
25
For each of the following cell types, listing (a) i important structural characteristic observed in the laboratory, and (b) the part that the structure complements or ensures.
shine musculus
a.________________________________________________
b.________________________________________________
shine muscle-
a) has a fusiform shape
b) allows the musculus to tense and relax.
26
For each of the post-obit jail cell types, listing (a) one of import structural feature observed in the laboratory, and (b) the part that the construction complements or ensures.
ruby claret cells
a._______________________________________________
b._______________________________________________
red blood cells-
a) biconcave shape
b) allows more surface area for efficient gas transfer.
27
What is the significance of the ruby blood cell being anucleate (without a nucleus)?
The red blood cell(rbc) does not take a nucleus. The lack of a nucleus enables the rbc to have more room to contain haemoglobin which increases its efficiency to carrying oxygen.
28
Red Blood Cell:
Did it ever have a nucleus? If so, when?
They did accept a nucleus . When they are formed in the bone-marrow, they contain a nucleus, but when the become mature it is replaced by haemoglobin in club to carry more oxygen.
29
Of the four cells observed microscopically (squamous epithelial cells, red blood cells, smooth muscle cells, and sperm) which has the smallest diameter? ________ Which is longest? _________
smallest: RBC
Longest: smooth musculus prison cell
30
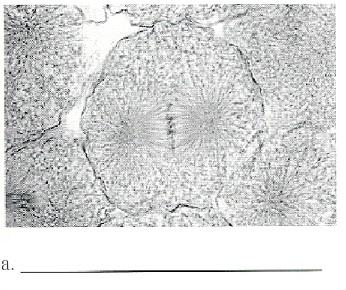
Identify the phase of mitosis in the post-obit photomicrograph.
31

Place the phase of mitosis in the post-obit photomicrograph.
32
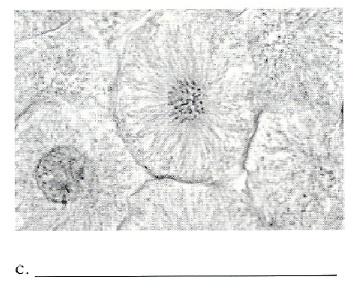
Place the phase of mitosis in the following photomicrograph.
33
What is the importance of mitotic cell partition?
The importance of mitotic cell division is to make a greater amount of cells for repair and growth while maintaining the aforementioned genetic makeup
34
Partition of the __1__ is referred to as mitosis. Cytokinesis is sectionalisation of the __2__. The major structural departure between chromatin and chromosomes is that the latter are __3__. Chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers by undivided structures chosen __4__.
1. Nucleus
2. Cytoplasm
3. Coiled/Condensed/Shortened
iv. Centromeres
35
If a cell undergoes mitosis simply not cytokinesis, the product is __5__. The construction that acts equally a scaffolding for chromosomal attachment and move is chosen the __6__. __7__ is the period of cell life when the cell is not involved in division. Two prison cell populations in the body that do not routinely undergo cell division are __8__ and __9__.
5. A binucleate cell or multinucleated jail cell
half-dozen. Spindle
7. Interphase
8. Skeletal
ix. Cardiac
Chromatin coils and condenses, forming chromosomes.
The chromosomes are v-shaped.
The nuclear envelope re-forms.
Chromosomes finish moving toward the poles.
Chromosomes line upward in the centre of the cell.
The nuclear envelope fragments.
The mitotic spindle forms.
Chromosomes first appear to be duplex structures.
Chromosomal centromeres are fastened to the kinetochore fibers.
The nuclear envelope is absent.
49
What is the physical advantage of the chromatin coiling and condensing to form short chromosomes at the onset of mitosis?
Curt, compact bodies easier to manipulate during mitosis rather than long, sparse chromatin threads.
stanfieldwhationam.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/2314
0 Response to "Exercise 4 Review Sheet the Cell Anatomy and Division"
Post a Comment